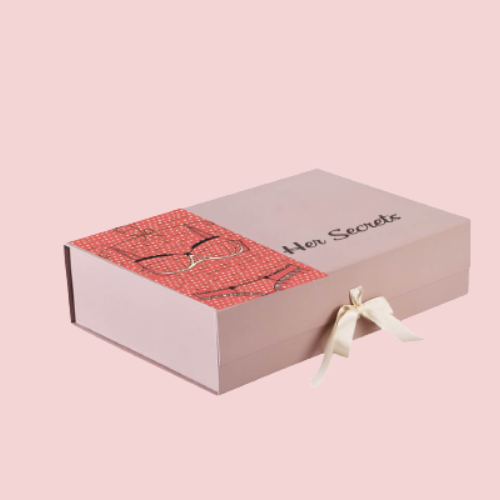
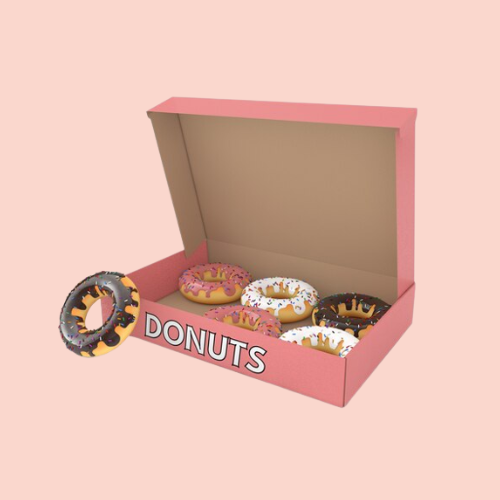
Offset printing, known for its exceptional quality and efficiency, is a highly sought-after process across many industries. CrownPackages understands the significance of impactful packaging, and that’s why we offer a variety of printing techniques, including offset printing. At CrownPackages, we leverage this technique to enhance the value of various products, packaging, and publications. Understanding how offset printing works can help you make an informed decision for your packaging projects.
What is Offset Printing?
Offset printing, or offset lithography, involves transferring ink from a plate to a rubber roller (or blanket) and then to various substrates. This method produces high-quality images and designs for mass production, making it ideal for printing large quantities of newspapers, brochures, stationery, magazines, and boxes.
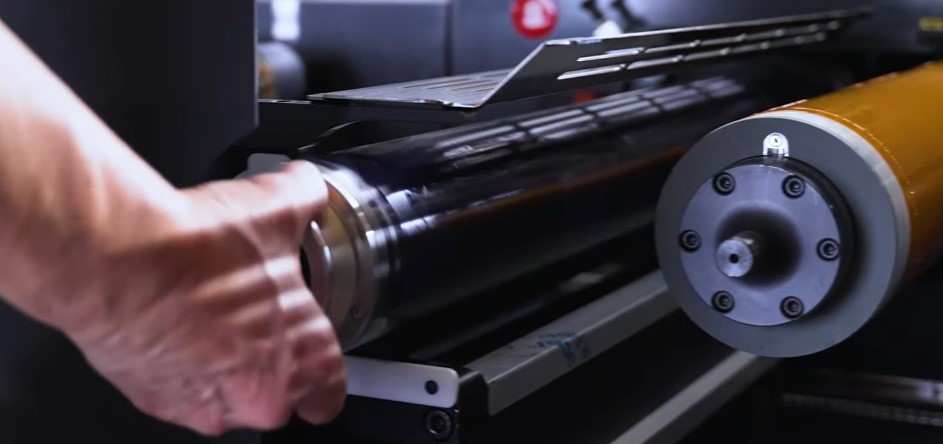

Why Choose Offset Printing for Packaging?
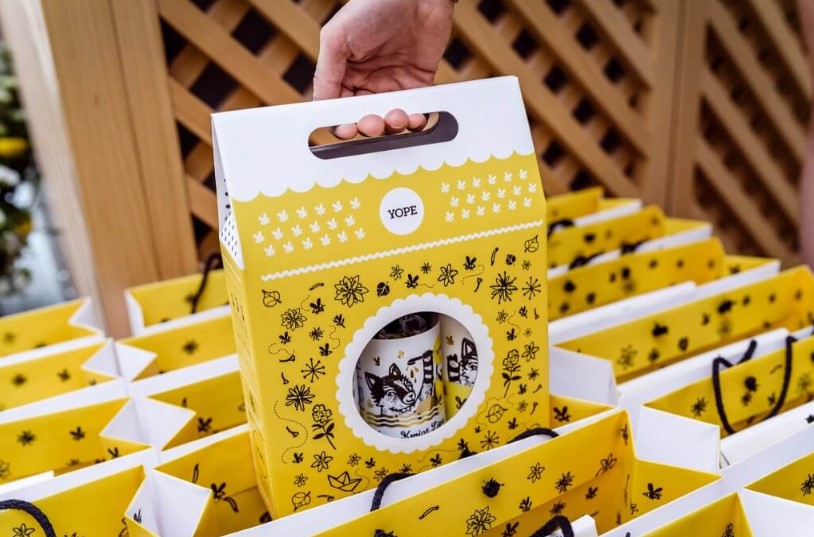

- Exceptional Quality: Offset printing delivers sharp, clear images and consistent color reproduction. Your packaging graphics will appear exactly as you envisioned, showcasing your brand and products in the best possible light.
- Versatility Unbound: This printing technique can be used on a wide range of materials, including paperboard, cardboard, and even some plastics. This flexibility allows you to create packaging solutions that perfectly suit your product’s needs.
- Cost-Effective for Large Volumes: While offset printing may have a higher initial setup cost, it becomes incredibly cost-effective for high-volume printing runs. The cost per unit decreases as the quantity increases, making it a budget-friendly option for large-scale projects.
- Consistent Results: Offset printing is renowned for its ability to produce consistent results throughout the entire print run. You can be confident that every piece of packaging will meet your exacting standards.
Offset Lithography vs Digital Printing
Offset and digital printing are distinct techniques with unique features and benefits. Here’s a comparison to help you understand the main differences:

- Printing Process: Offset printing uses plates to transfer ink onto a rubber blanket, which then applies the ink to the paper. Digital printing directly applies ink using an electronic file.
- Quality: Digital printing can produce good-quality images but does not match lithography’s sharp details and vibrant colors.
- Cost: Llithography offers reduced unit costs for large print runs, while digital printing is more economical for smaller runs.
- Turnaround Time: Digital printing has no plate setup time and offers a faster printing process.
- Customization: Digital printing allows for greater customization and personalization, including variable data printing, which offset lithography cannot achieve.
The Offset Printing Process at CrownPackages
At CrownPackages, we take pride in our meticulous offset printing process. Here’s a glimpse into the journey your packaging takes:
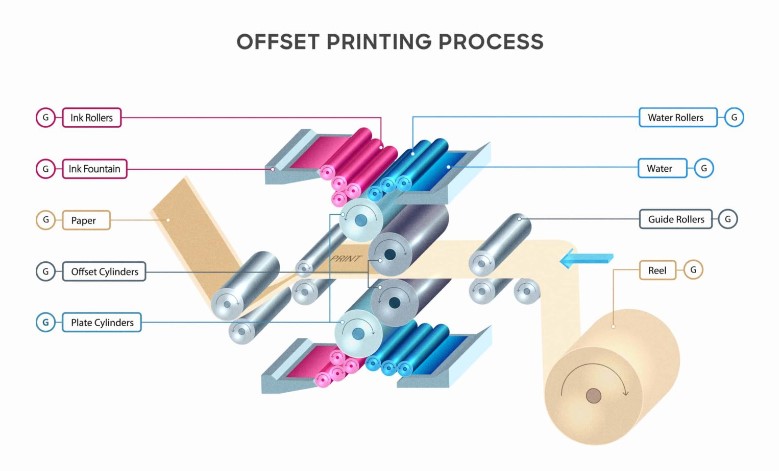
The Pre-Press Stage
The pre-press stage involves preparing digital files for the printing stage. Activities include designing, layout, and typesetting, ensuring that the final printed product meets the desired specifications. During this stage, designers verify fonts, formats, and color management to produce high-quality prints.
One common mistake is not converting work from RGB to CMYK, which ensures images are accurately colored and of high quality. Contact a CrownPackages product specialist to guide you through the pre-press stage, ensuring the printing process runs smoothly.
The Printing Stage
The printing stage uses specialized offset lithographic printing machines that transfer ink from printing plates to blanket cylinders and then to paper. This process is highly efficient and can handle various paper stocks, ink types, and printing plate sizes, producing high-quality prints with sharp, precise images and text.
The Post-Press Stage
The post-press stage includes finishing activities such as cutting and adding special coatings or embossing. Cutting involves trimming the edges of the materials to ensure uniform size and a neat, professional look. Finishing can include adding glossy or matte coatings for a polished appearance, or embossing to add texture and depth to the design.
Quality Control and Inspection
Quality control is crucial in ensuring the final product meets or exceeds customer expectations. Post-press technicians use various tools and techniques to inspect finished products, measuring color accuracy and consistency and closely examining for imperfections or defects.
Types of Offset Litho-Printing
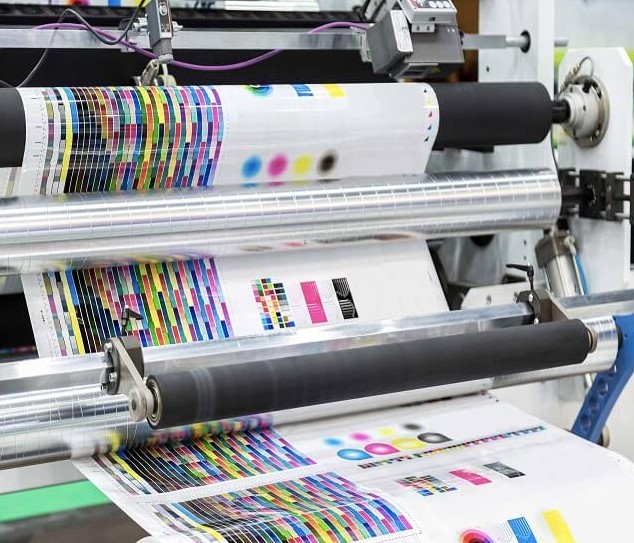

Web Offset Printing
Web lithography is typical for printing newspapers and boxes. Rolls of paper are fed continuously through the machine, producing over 5,000 printed materials. This method can produce over 3,000 papers per minute, making it ideal for large quantities with tight deadlines.
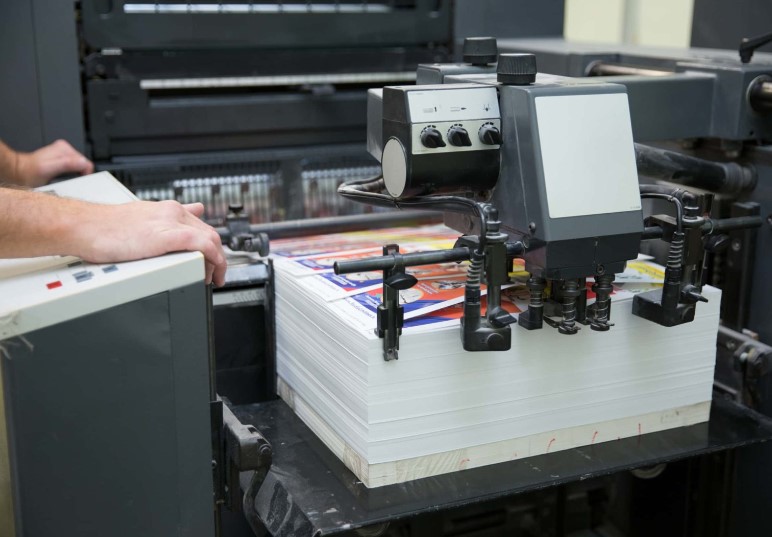

Sheet-Fed Offset Printing
Sheet-fed lithography produces smaller quantities, with sheets of paper fed individually to the machine. This method is quick and can produce up to 24,000 sheets per hour, making it a versatile option for various printing needs.
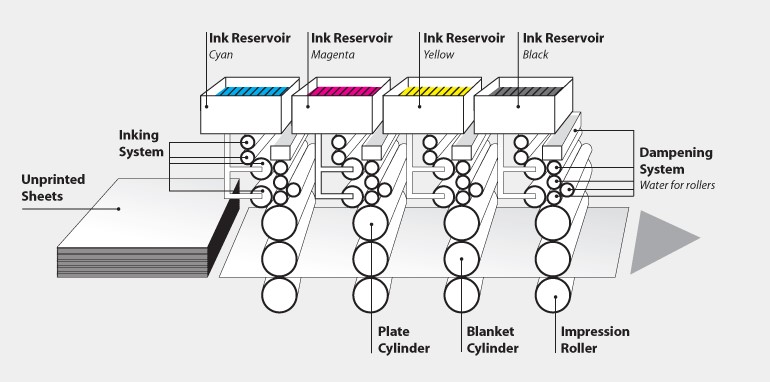
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Modern Offset Printing

Advantages
- Produces high-quality images and text with excellent color accuracy and sharpness.
- Suitable for various surfaces, including paper, cardboard, and plastic.
- Economical for large-scale production runs with lower setup costs.
- Ensures consistent results across large production runs.
Disadvantages
- Requires several steps, including preparing printing plates.
- Not ideal for highly customized designs.
- Not cost-effective for small production runs.
- Involves chemicals that require proper disposal to minimize environmental impact.
CrownPackages Your Partner in Exceptional Offset-Printed Packaging
At CrownPackages, we go beyond simply printing your packaging. We serve as your trusted partner throughout the entire process:

- Unmatched Expertise: Our team of packaging specialists possesses a wealth of knowledge and experience in offset printing. We’ll guide you through every step, from design considerations to material selection.
- State-of-the-Art Equipment: We invest in cutting-edge offset printing technology to ensure precise color reproduction, consistent printing, and optimal efficiency.
- Extensive Material Selection: We offer a vast array of paper stocks and other materials specifically chosen for their compatibility with this printing. This allows you to create packaging that is both visually stunning and structurally sound.
- Commitment to Quality: Quality is at the forefront of everything we do. Our rigorous quality control procedures ensure that your offset-printed packaging is flawless and reflects the high standards of your brand.
Conclusion
Offset lithographic printing remains a crucial and widely-used technique in various industries, including packaging. As technology evolves, offset printing will continue to offer innovative and visually appealing solutions. If you’re considering this method for your next packaging project, CrownPackages provides high-quality, versatile, and cost-effective prints that meet and exceed your requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is offset printing and how does it work?
Offset lithography is a multi-step process involving etched metal plates, water-repellent inks, water, blanket cylinders, and impression cylinders. The plates are designed so that oily inks adhere only to the image and text areas. This method ensures precise and high-quality printing.
How does the printing process work?
When the printer is turned on, a heater melts the ink. The text or image is projected onto the drum unit, similar to a laser printer. The melted wax is then dropped through a print head onto the drum unit. As the paper passes under the drum, the text or image is recreated on the page.
What is the process of creating an offset printing plate?
The process involves transferring or “burning” the print project, usually a digital file, onto four large, thin aluminum plates. One plate is prepared for each of the CMYK colors (cyan, magenta, yellow, and black). These flexible plates are then wrapped around the plate cylinder, ready for printing.
What is an example of offset printing?
Offset web printing is typically used for large runs, generally exceeding five or ten thousand impressions. Examples include newspapers, newspaper inserts, ads, magazines, direct mail, catalogs, and books.
What types of paper are used for offset printing?
The main types of paper used in offset printing are uncoated, gloss-coated, and matte-coated. Uncoated paper has a rougher, natural, non-glossy finish and is commonly used in manuals and books. Gloss-coated paper has a shiny finish, while matte-coated paper has a smooth satin finish, both often used in brochures and magazines.
What is the offset printing sequence?
In offset lithography, the common printing sequence is black, cyan, magenta, and yellow. This is also referred to as the color sequence or laydown sequence.
What is the difference between digital printing and offset printing?
Digital printing doesn’t use plates like offset printing. Instead, it uses toner (as in laser printers) or larger printers that use liquid ink. Digital printing is ideal for lower quantities, such as a run of 20 greeting cards or 100 flyers, offering flexibility and quick turnaround times.
Is offset printing a direct or indirect process?
Offset printing is an indirect printing process. A cylinder covered with a rubber blanket is positioned between the aluminum printing plate and the paper (or other substrate). The ink is transferred indirectly from the plate to the rubber blanket and then onto the sheet.




















